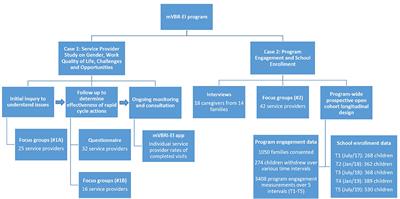
Background: This paper explores how implementation and refinement of an early intervention (EI) program for children with delayed development was informed by an iterative, intentional and structured process of measurement. Providing access to early intervention therapy for children in rural areas of India is challenging due to a lack of rehabilitation therapists and programs. Following a biopsychosocial framework and principles of community-based rehabilitation, a non-governmental organization, Amar Seva San gam (ASSA), overcame those barriers by designing a digital technology supported EI program in rural Tamil Nadu, India. Program objectives included providing service access; supporting program engagement, child development and school enrollment; and positioning the intervention for scale-up. This paper contributes to a growing body of literature on how program design and implementation can be informed through a cyclical process of data collection, analysis, reflection, and adaptation.
Methods: Through several strands of data collection, the design and implementation of the EI program was adapted and improved. This included qualitative data from focus groups and interviews with caregivers and service providers, and a mobile application that collected and monitored longitudinal quantitative data, including program engagement rates, developmental progression, caregiver outcomes, and school enrollment status.
Results: Measurements throughout the program informed decision-maki ng by identifying facilitators and barriers to service providers' quality of work-life, family program engagement, and school enrollment. Consultation with key stakeholders, including caregivers and service providers, and data driven decision making led to continual program changes that improved service provider quality of work-life, program engagement and school enrollment. These changes included addressing gender-related work challenges for service providers; forming caregiver support networks; introducing psychological counseling for caregivers; providing medical consultations and assistive devices; creating community awareness programs; improving access to therapy services; focusing on caregiver education, motivation and support; and advocacy for accessibility in schools.
Conclusion: The process of using evidence-informed and stakeholder driven adaptations to the early intervention program, led to improved service provider quality of work-life, greater program engagement, improved school enrollment and positioned the intervention for scale-up, providing lessons that may be beneficial in other contexts.